

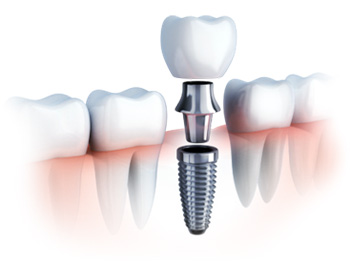
Dental implants are designed to provide a foundation for replacement teeth that look, feel and function like natural teeth. Implants are tiny titanium posts which are placed into the jawbone where teeth are missing. The bone bonds with the titanium, creating a strong foundation for artificial teeth. In addition, dental implants can help preserve facial structure, preventing the bone deterioration which occurs when teeth are missing.
Because dental implants behave in much the same way as the roots of natural teeth, they provide unrivaled stability for the placement of a broad range of dental prostheses, including crowns and bridges up to a complete set of teeth. For patients who wear full dentures, dental implants provide the added stability and retention required to improve comfort and fit while preventing any embarrassing slippage.
The long-term stability and success of a dental implant depend upon the presence of sufficient bone at the time of placement. In cases of periodontal disease or following the extraction of a tooth, bone volume is often lost. By placing a bone graft in the extraction site, or prior to the placement of a dental implant, we can establish sufficient bone support for a sturdy and stable dental implant.
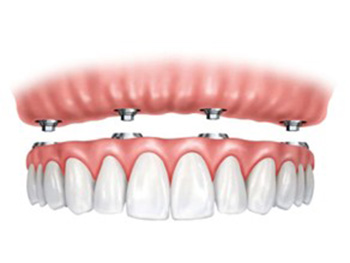
As the name implies, this type of denture attaches to a select number of strategically placed implants in the upper or lower jaw. These small surgical posts provide precise points of attachment for the overlying denture and add a significant measure of stability and retention.
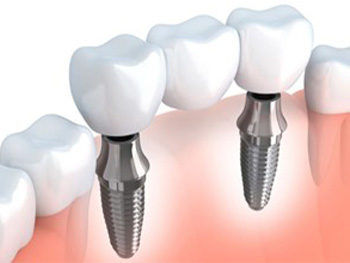
As the most advanced method for the replacement of missing teeth, dental implants come the closest to replicating the look, feel, and function of a natural smile. For this reason, an implant-supported bridge often represents the best option in care.
With an implant-supported bridge, there's no need to prepare, crown, or involve any adjacent natural teeth. Because dental implants behave in much the same way as the roots of natural teeth, they provide all the support a bridge requires.